

In the case of the UAE, qualified investors have varying definitions.
Generally speaking, most private funds can only be distributed to qualified investors.
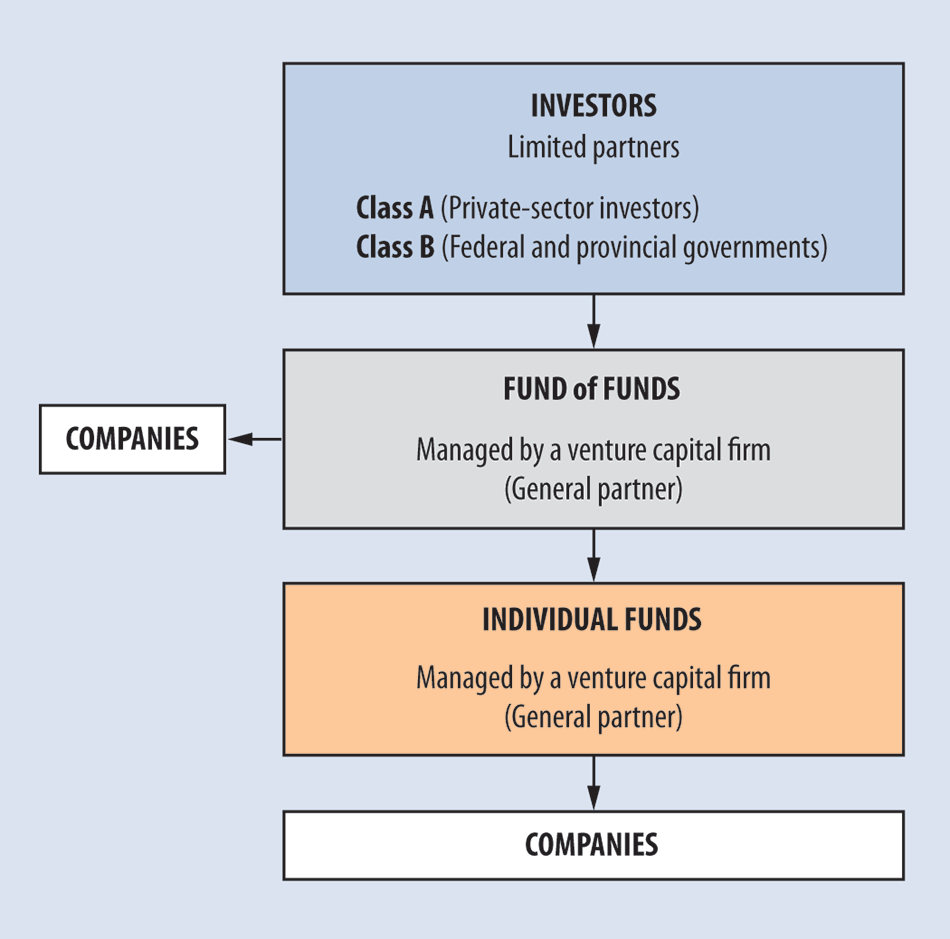
#Venture capital fund management professional
It also depends on the network of the placement agents and distributors, and their relationships with institutional and professional investors. Successful fundraising takes time and a successful closing is a factor of many variables, such as the economic outlook, the objectives and target sectors and geographies of the fund, and the track record and experience of the fund manager. For example, venture capital funds are typically structured to last at least ten years and may operate longer as they work to exit all of their portfolio companies.The lifecycle of a venture capital fund comprises: Venture capital investments have a long time horizon and are generally locked in until a liquidity event (for example, acquisition or initial public offering) when the venture capital firm and its fund investors hope to realize profits from their investment.

Venture funds typically invest in businesses in exchange for equity and some firms specialize in particular industries or in companies at a certain stage (for example, early, mature, or later stage). Registered investment advisers should reference Section 205(a) of the Investment Advisers Act and the rules thereunder for additional information on performance fee arrangements.Ī venture capital fund is a type of private fund that is managed by a venture capital firm, which may be required to register with the SEC as an investment adviser. The latter is often referred to as “carried interest.” These arrangements are often referred to by these percentages (e.g., a 2% management fee and 20% performance fee is referred to as “2 and 20”). See management fees definition above for examples of private equity fund fees.įor example, a private equity fund manager typically uses fee structure that includes a yearly management fee based on assets under management (e.g., 1%, 2%, etc.) and a performance fee based on the profits made above a certain benchmark (e.g., 10%, 20%, etc.). For example, carried interest is a type of performance fee, in the form of a portion of profits from an investment or investments, paid to private fund managers in venture capital and private equity firms. Performance fees are compensation provided to an adviser based on the performance of a client’s portfolio.Ī common way to calculate such fees is based on a percentage of investment profits. The footnotes to the financial statements often provide additional context and information to what is presented in the different financial statements. This differs from a company’s capitalization table, which tends to show the ownership as of a set date. Statements of shareholders’ equity show changes in the interests of a company’s shareholders over time.Cash flow statements show the company’s inflows and outflows of cash over a period of time (such as over the company’s fiscal year).Income statements show how much money a company made and spent over a specific period of time (such as over the company’s fiscal year).Balance sheets show at a fixed point in time (such as the end of the quarter or fiscal year) a company’s assets (what it owns that has value), its liabilities (what it owes to others), and its shareholders’ equity (what would be left for the shareholders if the company sold its assets and paid off all its liabilities).There are four main types of financial statements: They provide important insights to investors into where a company’s money came from, where it went, and where it is now. Financial statements are written records that communicate information about a company’s business activities and financial position.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
